1. Feature Overview
SIERA Expression Builder tool lets Admins create their own expressions that can be used to easily retrieve and manipulate data on any report. This is an evolving tool and presently helps users write basic aggregate functions with multi-conditions.
2. Prerequisites
SIERA is a paid feature. To enable it for your account, contact your account manager or support@leadsquared.com.
3. Expression Builder Rules
- A field in the expression builder has to be enclosed with backticks. For example,
`data_source_name.field_name`. - The field name has to be appended with the entity. For example,
`Leads.Lead Stage`. - The values for a string have to be in single quotes. For example,
'string'. - An array of values must be enclosed in square brackets. For example,
['Value 1', 'Value 2']. - SIERA stores empty date values as 01-01-1925. If you want to write an expression with null date values excluded, use
ToYear(<date field>) > 1925. Similarly,ToYear(<date field>) <= 1925will filter rows with date values not defined. For example,CountDistinctIf(`Leads.Prospect ID`, ToYear(`Leads.Date of Birth`) > 1925)will return leads who have a defined date of birth.CountDistinctIf(`Leads.Prospect ID`, ToYear(`Leads.Date of Birth`) <= 1925)will return leads where the date of birth is not defined.
- Clicking on a tab will enter the selected function from the expression builder.
4. Types of Expressions
Expressions in SIERA are of 3 types –
- Aggregated Expressions – An aggregate expression uses an aggregate function to summarize a selected metric. These include expressions like Count, CountDistinct, Sum, Min, Max, and Avg.
- For example, if we want to get a count of leads, we can use the expression
Count(<field name>).
- For example, if we want to get a count of leads, we can use the expression
- Conditional Expressions – Conditional expressions use aggregate functions along with conditions.
- For example, if you want to Count leads only if they are from Google and Facebook, using an expression of Count() will not work. In this case, we can use
CountIf(<condition>).
- For example, if you want to Count leads only if they are from Google and Facebook, using an expression of Count() will not work. In this case, we can use
- Calculated Values – Calculated Values are a combination of 2 or more expressions (aggregated or conditional) on arithmetic functions like +, –, *, or /.
- For example, if we want the percentage of leads from Google and Facebook over total leads, we can use
(Countif(<condition>)/Count(<field name>))*100. Calculated Values do not support drill-down in the reports or dashboards.
- For example, if we want the percentage of leads from Google and Facebook over total leads, we can use
5. Navigate to Expression Builder
Follow the steps below to navigate to the expression builder:
- Click Create Report.
- Select a Data Source.
- Click the + Add Values button.
- Click + Custom Values.
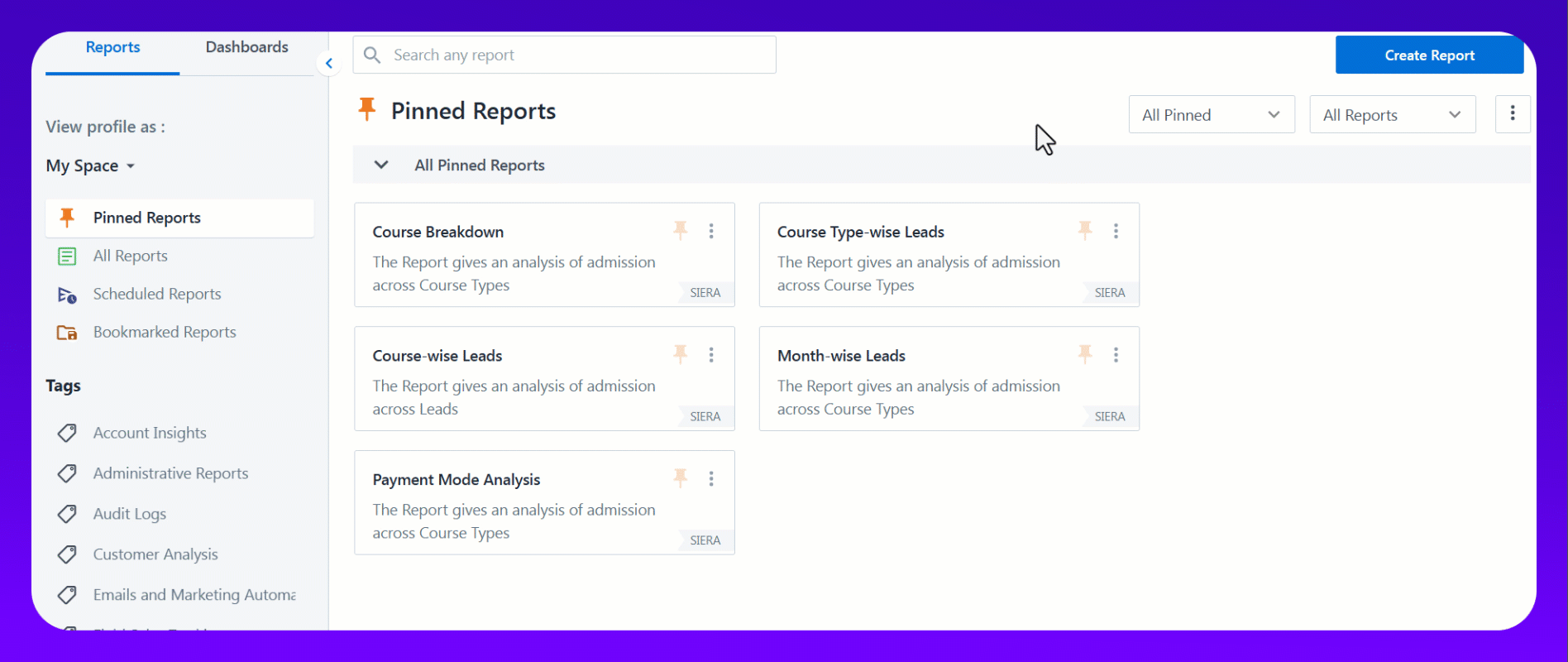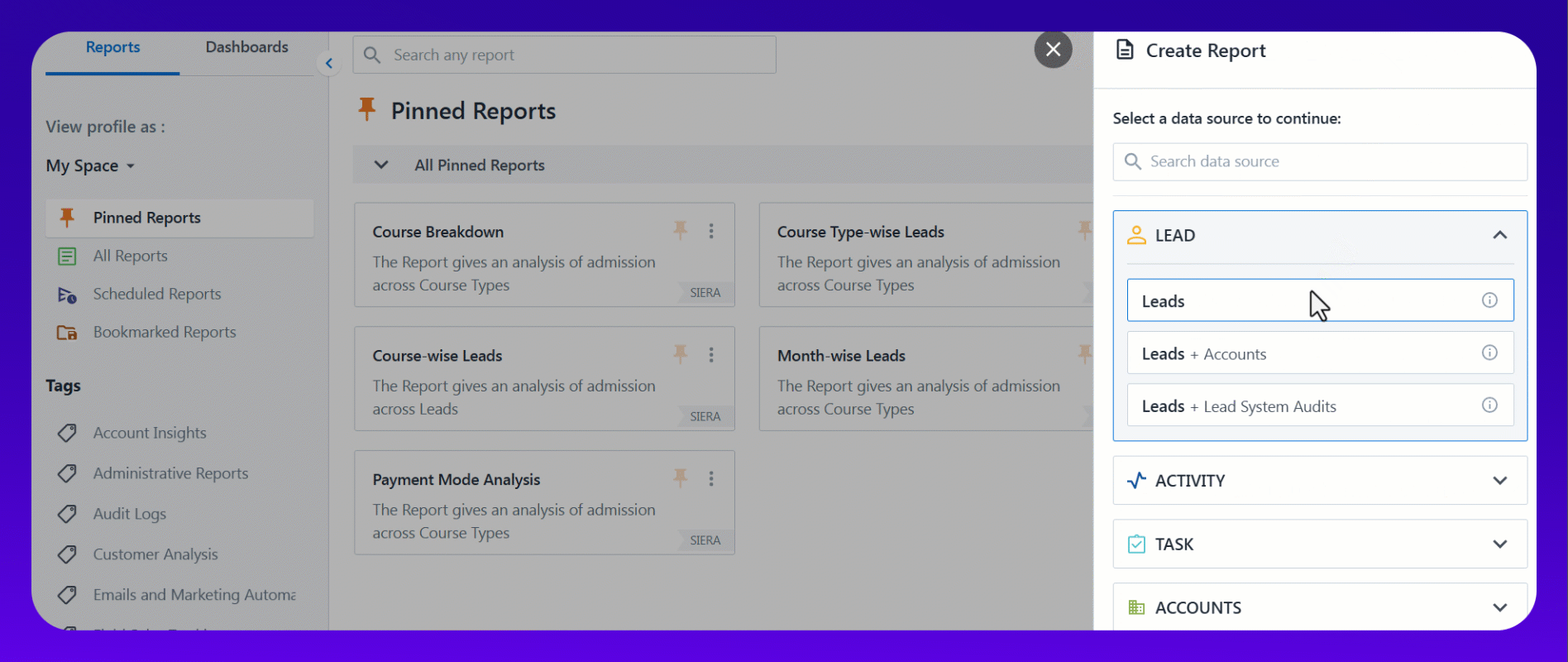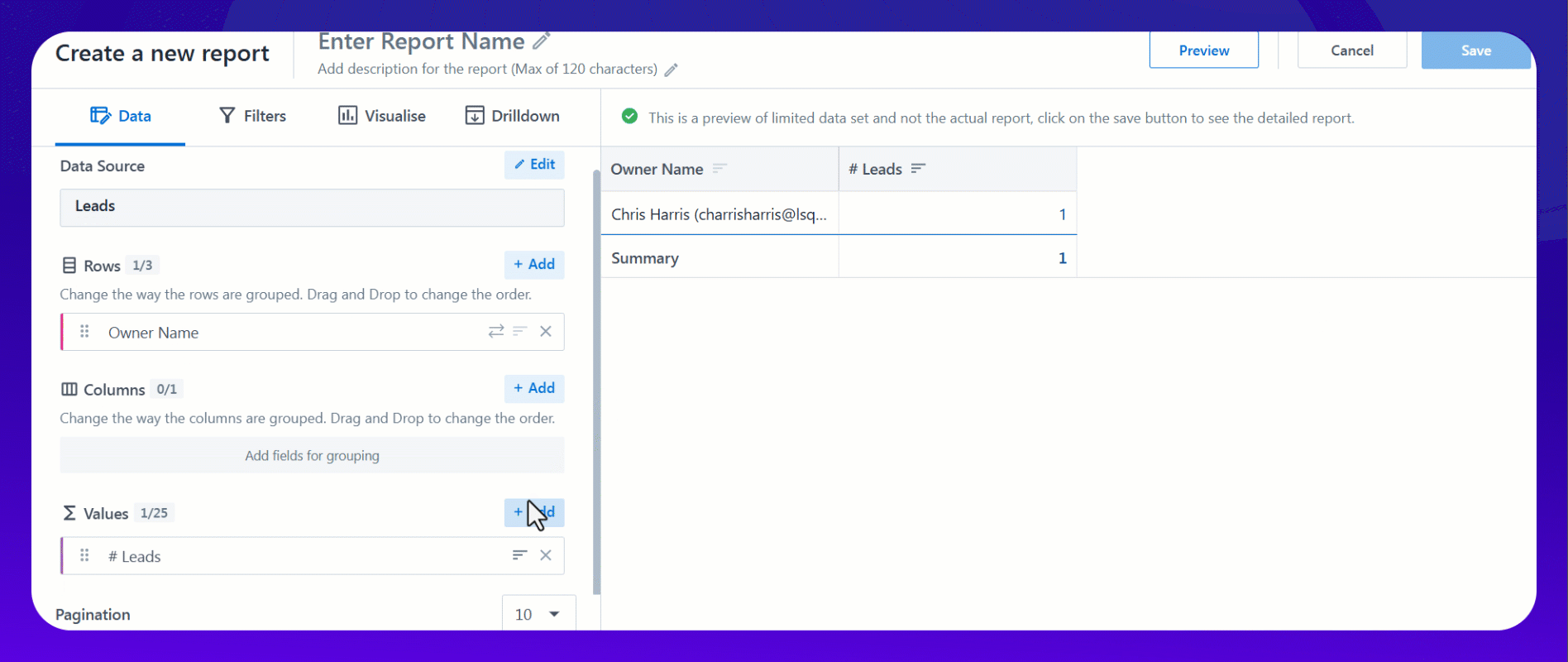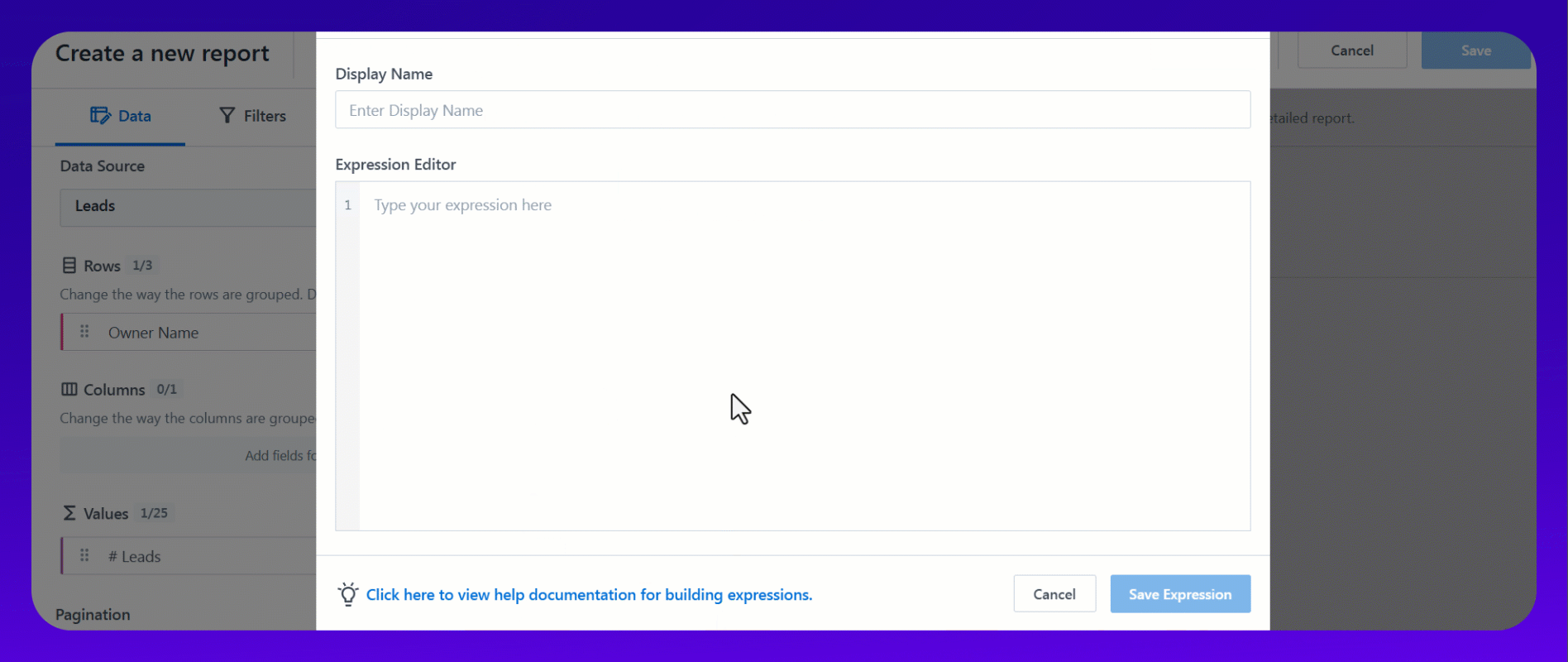
This sections below will help you understand the syntax and usage of various functions available for building expressions.
6. Operators, Conditions, and Constants
| Function & Example Expression |
| Equal – Used to compare if 2 values or fields are equal.
|
| Not Equal – Used to compare if 2 values or fields are not equal.
|
| Less Than – Used to compare if a value or field is less than compared to another value or field.
|
| Less Than or Equal – Used to compare if a value or field is less than or equal to another value or field.
|
| Greater Than – Used to compare if a value or field is greater than compared to another value or field.
|
| Greater Than or Equal –Used to compare if a value or field is greater than or equal to another value or field.
|
| in – Used to determine whether the value exists in a list of values.
|
| notin – Used to determine whether the value does not exist in a list of values.
|
| Text Constant – Text constant to be written as ‘Text’, with quotations.
|
| Number Constant – Text constant to be written as 50, without quotations.
|
| Addition – Used to add two values in your report. Fields (Number type) and constants can be used as operands
|
| Subtraction – Used to subtract two values in your report. Fields (Number type) and constants can be used as operands.
|
| Multiplication – Used to multiply two values in your report. Fields (Number type) and constants can be used as operands.
|
| Division – Used to divide two values in your report. Fields (Number type) and constants can be used as operands.
|
7. Logical Expressions
| Function & Example Expression |
| and – An and expression returns true if all of its operands are true. The and expression will work if there is more than 1 expression inside it. For example, let’s say you want to return TRUE when a Lead has converted (Stage is Customer) and if the Source is either from Referral or Affiliate.
|
| or – An or expression returns true if any of its operands are true. The or expression will work if there is more than 1 expression inside it. For example, let’s say you want to return TRUE when a Lead has converted (Stage is Customer) or if the Sub-stage is either Converted or Paid.
|
8. Aggregate Expressions
| Function & Example Expression |
SUM The Sum function allows you to calculate the sum of numeric values within a given field. For example, if you want to create the calculated column which stores the sum of the field mx_Custom_2. We can use the Expression Builder to write the expression.
|
| SumIf The SumIf function allows you to calculate the sum of numeric values within a given field along with some conditions. For example, if you want to create the calculated column which stores the sum of the field mx_Custom_2 when Stage is “Customer”. We can use the Expression Builder to write the expression as given.
|
| Count The Count function lets you count the number of occurrences of a specific value or field within a given range. For example, let’s assume you want to create the calculated column which stores the count of the leads.
|
| CountIf The CountIf function allows you to count the number of occurrences that meet a specific condition. For example, you can create a calculated column that stores the count of the leads when the lead stage is ‘Prospect’.
|
| CountDistinct The CountDistinct function allows you to count the unique number of occurrences that meet a specific condition. For example, you can create a calculated column that stores the count of unique leads.
|
| CountDistinctIf The CountDistinctIf function allows you to count the distinct number of occurrences that meet a specific condition. For example, you can create a calculated column that stores the count of distinct leads when the lead stage is ‘Prospect’.
|
| Max The Max function allows you to calculate the maximum of numeric values within a given field. For example, you can create the calculated column which stores the maximum of the field mx_Custom_2.
|
| Min The Min function allows you to calculate the minimum of numeric values within a given field. For example, you can create the calculated column which stores the minimum of the field mx_Custom_2.
|
| Avg The Avg function allows you to calculate the average of numeric values within a given field. For example, you can create the calculated column which stores the average of the field mx_Custom_2.
|
| MaxIf The MaxIf function allows you to calculate the maximum of numeric values within a given field along with some conditions. For example, you can create the calculated column which stores the maximum of the field mx_Custom_2 when Stage is ‘Prospect’.
|
| MinIf The MinIf function allows you to calculate the minimum of numeric values within a given field along with some conditions. For example, you can create the calculated column which stores the minimum of the field mx_Custom_2 when Stage is ‘Prospect’.
|
| AvgIf The AVGIF function allows you to calculate the average of numeric values within a given field along with some conditions. For example, you want to create the calculated column which stores the average of the field mx_Custom_2 when Stage is ‘Prospect’.
|
9. Date Time Expressions
| Function & Example Expressions |
| DurationAdd The DurationAdd function allows you to add any duration to a particular date field. Allowed Units – second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, year Returns – Added Duration (DateTime) For example, you can create the calculated expression which counts the lead which came into the system 4 months ago and the current stage is not ‘Customer’.
|
| DurationSubtract The DurationSubtract function allows you to subtract any duration from a particular date field. Allowed Units – second, minute, hour, day, week, month, quarter, year Returned Value – Subtracted Duration (DateTime) For example, you can create the calculated expression which counts the lead which came into the system 4 months ago and the current stage is not ‘Customer’.
|
| CurrentDateTime The CurrentDateTime function returns the current date and time. For example, you can create a calculated column that stores -4 months from date field mx_Custom_2.
|
| ToHour The ToHour function allows you to extract the hour component of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: Hour Component (Number) eg: 23 For example, you can write a condition where you want to count the leads which came into the system at 11 PM.
|
| ToYear The ToYear function allows you to extract the year component of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: Year Component (Number) eg: 2023 For example, you can write a condition where you want to check if the year component of the datetime field is equal to 2023.
|
| ToYearWeek The ToYearWeek function allows you to extract the week and year components of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: Week and Year Component (1-53 Number) Eg: 202345 (45th Week of 2023) For example, you can write a condition where you want to check if the week and year component of the datetime field is equal to the 45th Week of 2023.
|
| ToMonthOfYear The ToMonthOfYear function allows you to extract the month component of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: Month of the Year (1-12 Number) eg: 1 (for January) For example, you can write a condition where you want to check if the month component of the datetime field is equal to January.
|
| ToDateOfYear The ToDateOfYear function allows you to extract the date component of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: Date of the Year (1-366 Number) eg: 32 For example, you can write a condition where you want to check if the date component of the datetime field is equal to 2nd Feb.
|
| ToQuarterOfYear The ToQuarterOfYear function allows you to extract the quarter component of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: Quarter of the Year (1-4 Number) eg: 2 For example, you can write a condition where you want to check if the hour component of the datetime field is equal to 2nd Quarter.
|
| ToMonth The ToMonth function allows you to extract the month and year components of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: yyyy-mm-01 (String) eg: ‘2023-02-01’ For example, you can write a condition where you want to count the leads created in the month of February 2023.
|
| ToQuarter The ToQuarter function allows you to extract the quarter and year components of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: YYYY QX (String) eg: ‘2023 Q2’ For example, you can write a condition where you want to count the leads created in the 2nd Quarter of 2023.
|
| ToDayOfWeek The ToDayOfWeek function allows you to extract the day of the week component of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: 1-7 (Number) Range: (1-7: Monday = 1, Tuesday = 2, …, Sunday = 7) eg: ‘6’ for Saturday For example, you can write a condition where you want to count the leads created on Saturdays.
|
| ToWeek The ToWeek function allows you to extract the week and year components of any datetime(timestamp) field. Returned Value: YYYYWW (Number) eg: 202347 For example, you can write a condition where you want to count the leads created on the 47th Week of 2023.
|
| DateUnitDiff Returns the count of the specified time unit boundaries crossed between the start and end dates. This can be used to create TAT between 2 date fields. Returned Value: (Number) eg: 43
Accepted Intervals –
The above expression will calculate the TAT for each grouping on average. For cases when there is no value in the date field, the expression builder will take the value of 01-01-1925. To exclude cases where there is no payment done, use the syntax below-
|
| ToDate Returns the date component from a datetime field. Returned Value: (String) eg: 2023-10-03 For example, you can write a condition where you want to count the leads created on 2023-10-03
|
10. Custom Dimensions
| Function & Example Expressions |
| If Returns a string based on a condition. The condition can be nested. Returned Value: (String) e.g., ‘Hot’, ‘Medium’, ‘Warm’, ‘Cold’ For example, let’s assume we want to classify leads based on their ProspectStage into ‘Hot’, ‘Medium’, ‘Warm’, or ‘Cold’ categories.
|
Any Questions?
If you have any questions related to Expression Builder that weren’t answered here, please leave comments below. We’ll be happy to help!






I need Help, I am creating a report, In rows, I have partner names, in values, I have Number of leads from respective partners are coming. Now, I need one more column, I which I want to show % of leads from respective partners. How can I get sum of all the leads from all the partners.
1st column I am getting correctly, but for second one, I don’t know How to get the total opportunity value from summary.
Hi. At present, this feature isn’t supported on SIERA, but should be available in a future release.
Hey, is there a ‘like’ function in SIERRA? Like how it works in SQL
Eg: first_name like ‘%raj%’ so it will pull all first_names that have raj
Hi. At present, this functionality isn’t available. But I’ve passed this on to the product team as a feature request.
Hi, I’m trying to figure out how if statements work in SIERRA?
Basically I have two columns connected disposition and not connected disposition and I want to combine both so I want to write an IF statement – if connected is null then not connected else connected – basically an ifnull. But it does not seem to work.
Ref: If(
Activity.mx_Custom_1= Null,Activity.mx_Custom_2,Activity.mx_Custom_1)Hi Ishan. You might need to replace
Nullin the expression with an empty string (''). Could you try the expression below and let me know if it works?If(Activity.mx_Custom_1 = '', Activity.mx_Custom_2, Activity.mx_Custom_1)If I want to count on basis of data contains specific character, then how to use it SIERA.
For Example: Column1 has following data
A123
12C4
H543
8890
GHS0
9430
I want to count if data contains “4″ then output will be 3 (i.e. 12C4, H543, 9430)
How to do this in SIERA
Hi, Ajay. At present, you can’t execute such a query. But I’ve communicated this as a feature request to the team.
Is there any function like starts with specific character
For Example: Column1 has following data
A123
12C4
H543
8890
A783
GHS0
9430
I want count of output where data startswith “A” i.e. A123, A783.
Hi, Ajay. As mentioned before, this functionality isn’t available yet.
Is there any alternative of this functions so we can use it to create Dashboards
There aren’t any alternatives available at the moment.